How To Manually Add Structured Data Markup to your WordPress Site

Table of Contents
Introduction
Structured data markup is a text format that is added to your webpage HTML so Google can make sense of the content. By adding structured data to your web pages, it provides Google with detailed information that classifies the content, and in return, it appears as a Rich Result.
Rich Results, also known as Rich Snippets, appear in Google results with more details, such as recipes for food dishes, reviews for a product, job listings and much more.
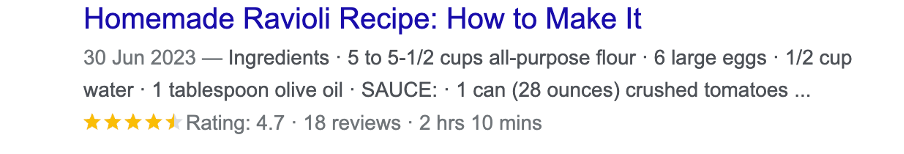
By adding structured data it can provide users with more information, which, in turn, can lead to a higher click-through rate. Therefore, adding this to your website will help attract more visitors.
Structured Data Types
Before making any modifications to your website, you must identify which type of data you want to include on your web pages.
There are plenty of different types available, such as Books, Reviews, FAQ, Local Business and much more. Visit Google documentation and click on one of the features. Here, it will provide you with information on how the structured data works, different components you can add to it, along with an example of the JSON structure data snippet.

Review the JSON-LD snippet for that feature, then copy the text it to your favourite code editor.
Modify the JSON text to suit the content of your web pages. As an additional measure, ensure the JSON is free from any syntax errors. I use jsonlint.com to check this. Copy your code to Jsonlint and click ‘Validate JSON’.
When you are satisfied with it, it’s time to add it to your WordPress site.
Applying Structured Data to your WordPress Site
Now, you need to add the data to the HTML head of each webpage on your site. Without editing the core theme files of your website, you need an easy way to achieve this. To do so, download and activate a WordPress plugin called Headers and Footer Scripts. This is a lightweight plugin that allows you to input your structured data into the head of each webpage.
Next, locate and edit one of your web pages, and scroll down until you see the ‘Insert Script to <head>’ section.

Enter your structured data here and click ‘Update’.
Testing
After you have successfully added structured data to all your relevant web pages, you need to test it to ensure it’s working correctly.
Google provides an excellent tool for this purpose called Rich Results Test.
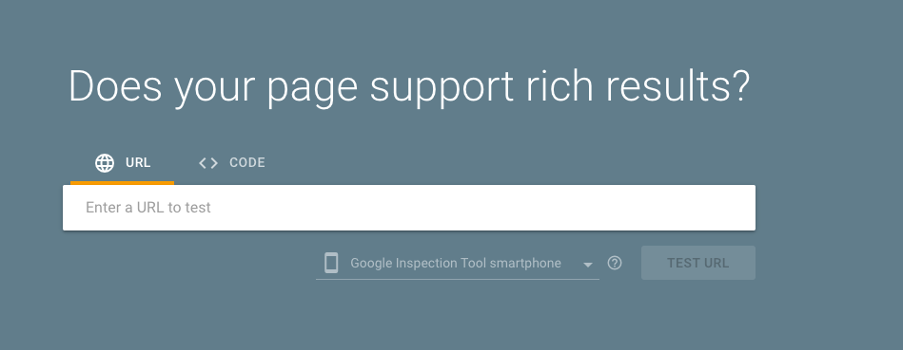
Enter the URL for one of the webpages where you’ve applied changes to, and click ‘Test URL’.
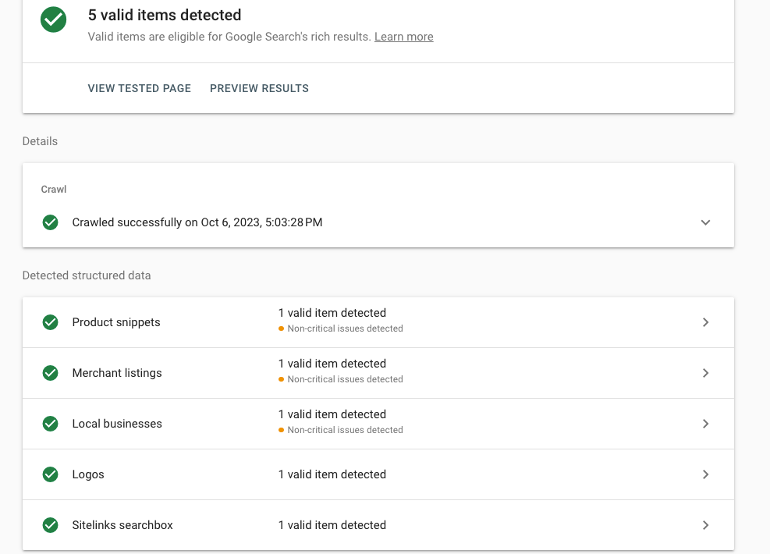
After the test is complete, it will provide messages to notify you if your changes have been applied successfully. It will also show you if there are any errors and provide guidance on how to fix them.
Perform this test for every webpage where you have added JSON text.
Conclusion
While there are many WordPress plugins available for this purpose, if you prefer not to add extra bloatware to your website, follow these steps, and you’ll be able to manually add structured data to your website within 30 minutes.
If this process seems cumbersome and you’d rather have a professional review your website to determine if your services and products are optimised for rich snippets, then schedule a free SEO audit with us.
How to Perform an SEO Audit

Table of Contents
Introduction
An SEO audit should be the first thing you do when you decide to optimise your website. By performing an SEO audit, you can better understand the work that needs to be done, allowing you to create an action plan.
1. Basic
Website Listed on Search Engine
The very first step is to check which pages on your website that Google knows about. This is a very simple task to carry out:
Go to Google and type in your website address like this site:<yourwebaddress>.com

This will return all the web pages Google is aware of. Check through each result and confirm if the web pages you are aware of are listed.
If, however, you find webpages not listed here, then you may have an indexing problem. Go to your Google Search Console and review if there are any indexing issues.
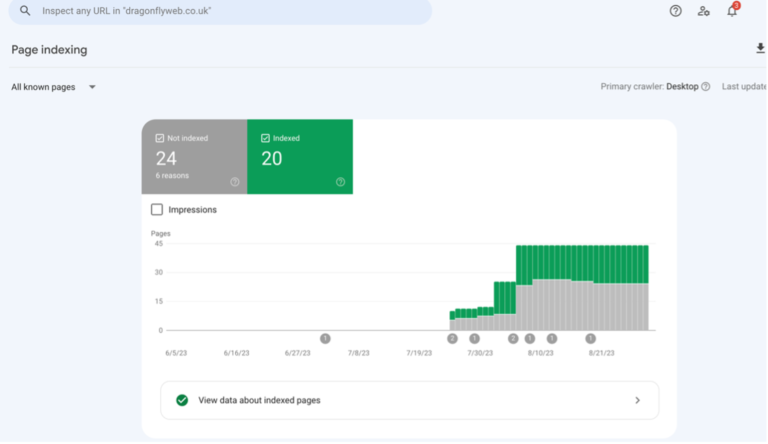
Some of the common indexing errors are:
• 404
• Soft 404
• Excluded by no index tag
• Duplicate based on canonical
• Blocked by robots.txt
Check out Google’s webpage on how to fix these issues.
You should also submit a sitemap, which allows you to help search engines crawl and index your web pages. To create a sitemap, there any many tools out there to help with this. Once created, submit it on Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster.
Check Website Traffic
To establish your starting point, you need data about your current standing to use as a baseline.
Navigate to Google Analytics, then go to Reports > Generate Leads > Traffic Acquisition.
From this point, take note of the number of Organic Search. You will want to monitor this closely in the future.
Broken Links
Broken links are detrimental to SEO, as Google considers them a poor user experience.
You’ll need a tool like Screaming Frog to check for broken links. Enter your website domain name in Screaming Frog, then click “Start”. Once complete, go to the URL tab and review any web pages with a status code 404.
If the webpage is not needed, simply delete it. However, if the webpage has many backlinks, you do not want to lose all that link juice. In this case, create a redirect (301) to another functioning webpage.
Dead Pages
When you performed the first step, “Website listed on Search Engine”, you may have noticed webpages you never knew existed. These web pages were probably created when you first developed your website or were automatically generated when configuring other aspects of your website.
If any web pages provide no value and don’t have a load of backlinks pointing to them, simply delete them.
Mobile Friendly
I don’t have to tell you that a vast number of users use their mobile devices to search the internet. Consequently, Google is encouraging people to design and develop their websites with a mobile-first approach.
When performing an SEO audit, utilise Google’s Mobile-Friendly Testing Tool to check if your website is mobile-friendly.
Simply enter your domain URL, and the tool will inform you if your website is suitable for mobile devices.
If your website is not optimised for mobile, consider using a responsive design or theme and incorporating the meta name=”viewport” tag on your web pages.
2. On-Page
URL
Use clear and concise URLs, as this helps users understand what the page is about. From an SEO perspective, it is also a good idea to include a keyword in your URL.
For existing websites, you should be cautious about changing live URLs as this can negatively impact your SEO health.
Title Tag
The title tag is one of the most crucial aspects of on-page SEO. It represents the highlighted text that appears in search results. Google uses the defined keyword in the title tag for ranking purposes. Therefore, ensure you include the keyword you want to rank for in the title tag.
Include only one keyword and do not repeat the keyword.
You shouldn’t make the title character length excessively long; aim to keep it under 60
Heading Tags
These are the HTML heading tags that appear on the web pages. Ensure that you don’t use the same text for your H1 tag as you do for your title tag.
Include an H1 tag for the web page title and incorporate your keyword. Make sure you only have one H1 tag, as search engines can become confused if there are too many H1 tags. For the rest of the page, use the remaining heading tags.
Additionally, ensure that the heading tags appear in descending order on the rest of the page.
Meta Tags
The primary meta tag to focus on is the Meta description. While the Meta Description doesn’t carry as much weight as it once did, it’s still a good practice to include a meaningful page description.
You do not want your meta description too long, as it may not display correctly on the results page. Conversely, you do not want it to be too short, as it won’t provide enough information. Aim for 150 – 160 characters.
Links
Let’s focus on internal links. Internal links are essential and provide significant benefits for search engines. They assist both users and search engines in understanding your site better. Additionally, they help direct link juice towards more important web pages.
Use a few internal links on a web page, pointing them towards the crucial pages on your site. Write meaningful anchor texts that align with the content you are creating and the destination of that link.
When it comes to external links, also include a few of them as referencing high-authority sources can enhance trustworthiness.
Images
Images play a role in search engines, as some searches prioritise visual content.
To help search engines discover your images, use the correct HTML elements such as <img> or <picture> tags.
Utilise alt text to provide textual descriptions and use descriptive file names, for example “red-yoga-mat.jpg.”
Consider using image sitemaps to assist search engines in finding and indexing your images.
Schema Mark Up
Schema markup, or structured data markup, consists of pieces of data that you add to your web pages to provide additional information such as services, products, business, etc. This helps search engines better understand the content of your website.
You can create a schema markup manually or use a tool to generate it. Google provides a testing tool so you can see if the structured data markup has been applied correctly.
Content
This part of the audit aims to review the current content on the website. It is a good idea to look at the content when performing an SEO audit. Some of the things you should be looking for:
• Does the website address the reader’s intent effectively?
• Does it feature a compelling introduction?
• Are there short blocks of text for easy readability?
• Are there enough images to break up the text and page sections?
• For articles or blogs, does it include a table of contents?
• Does it feature a FAQ?
• Are keywords included in the first 100-150 words of the page?
• For blogs, are there enough external links to authoritative sites?
Make a note of all necessary actions and create a plan to address them.
3. Technical
HTTPS
HTTPS is a security protocol that ensures the security of all transactions between a user and the website. It has become the standard for most websites and is typically in basic domain hosting packages.
Checking for HTTPS on a website is straightforward. When you open a website, you can verify it by looking for the padlock icon in the URL bar.

If you notice anything different, contact your web hosting company.
Website Structure
Having a well-organised website structure is immensely beneficial for SEO. It aids search engines in locating and crawling your website while providing users with easy navigation.
You should aim for a flat-style model that doesn’t extend beyond 3 or 4 layers deep.
Review each layer of the website to determine if any changes can be made. On established websites, making structural adjustments may be more challenging than on new websites.
Domain Accessible
You need to ensure that your website is accessible only on one domain. If users can access your website from multiple locations, it can lead to a number of indexing issues.
Utilise a tool like httpstatus.io, to confirm everything works.

Custom 404 Pages
To enhance your SEO, you want to create a custom 404 page that aligns with your brand. To check if your website has a custom 404 page, type in some random gibberish letters after the domain name e.g., drgonflyweb.com/blahblahblah
Website Performance
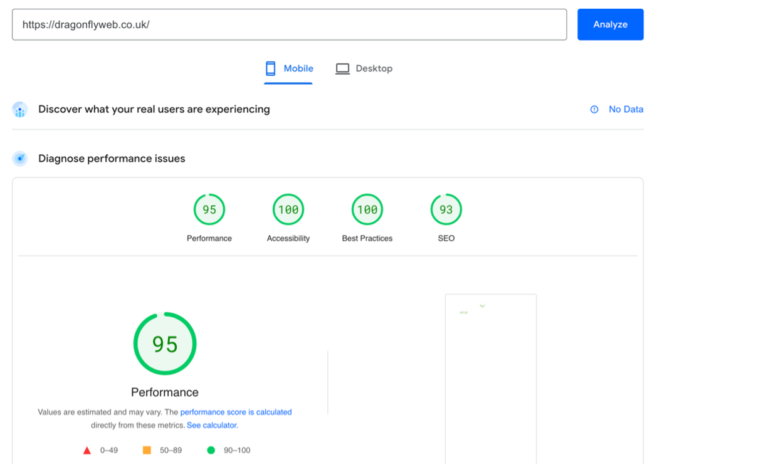
Website performance is a critical aspect of SEO. It is crucial to ensure your website is operating at its best. Search engines won’t rank your website highly if it’s slow and has bugs.
Analyse your website using Google’s performance checker tool. This tool provides metrics in several areas but pay special attention to the ‘Performance’ category. Review and address any issues to ensure your website performs well and achieves a green score.
4. Link Building
Review Backlinks
In this process of an SEO audit, you want to assess the backlinks currently pointing to your website. This task is essential for identifying broken backlinks and evaluating whether any backlinks are doing more harm than good.
Competitor Backlinks
Utilise a tool like Semrush to identify your competitor’s backlinks. You want to determine if there are any backlink opportunities you can leverage. This might include identifying broken links to your competitor’s website or finding opportunities to create even better content than your competitors.
After analysing the opportunities, reach out to the domain owners to propose a backlink to your website. It is essential to keep track of these opportunities and your journey.
5. Keywords
Review Keywords
Just as with reviewing backlinks, you should assess which keywords your website is organically ranking for. Take note of any irregularities, such as keywords you were unaware of, pages ranking for unintended keywords, and any missing keywords.
Keyword Tracking
It is a good idea to track keywords going forward and set up automated notifications. For any keywords you want to target, keep a record of their SERP positions and mark them to monitor regular updates. If the keywords are not ranking as expected, you need to review and adjust your methods.
Conclusion
This article should provide you with a solid foundation on how to perform an SEO audit. There are areas where you can delve deeper, but that will depend on the size and complexity of the website.
Dragonfly Web provides a full suite of services along with a free SEO audit. Feel free to get in touch to see how we can assist you.
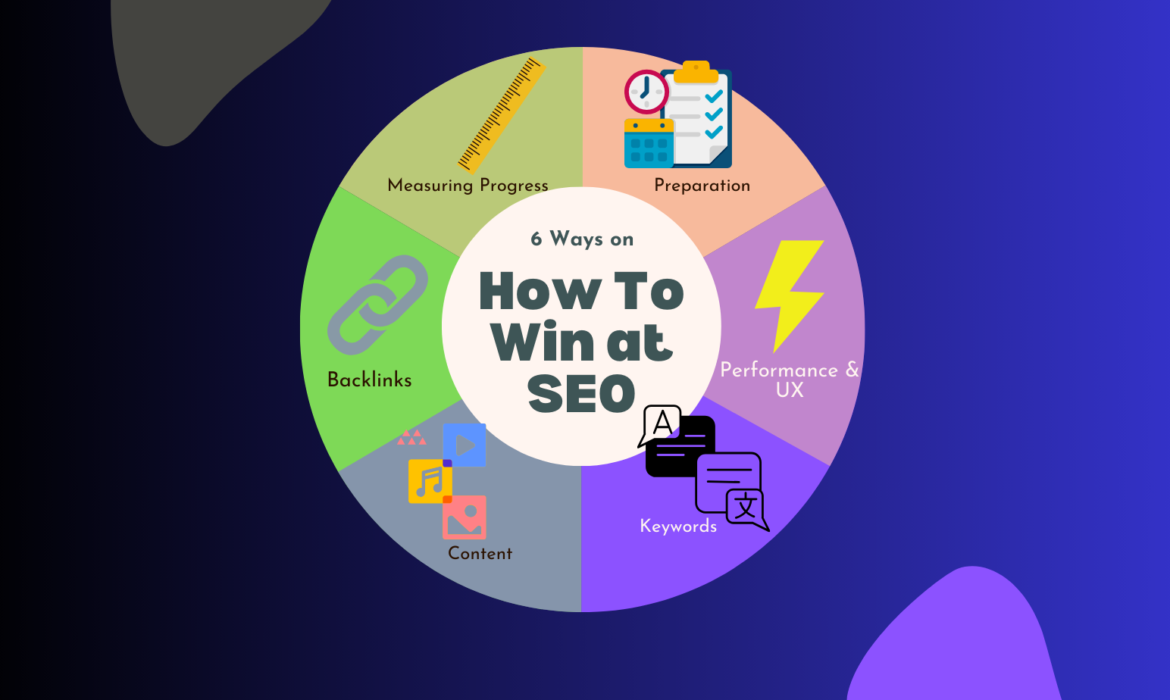
6 Steps on How To Win at SEO (2023)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Search Engine Optimisation otherwise known as SEO, is the process of optimising your website both internally and externally to perform better in organic search results.
It’s already well-known that the majority of online experiences begin with a search engine, and organic search is still the number one way of driving traffic to your website compared to any other digital marketing medium. So, it is extremely beneficial always to have an SEO campaign at the forefront of your business.
When starting with SEO, it can get overwhelming, so we have broken it down into various topics below.
1. Preparation
At the very start, you want to do some initial checks, which include gathering data about the digital presence of your website and identifying any technical issues.
To gather data about your website and its current state of visibility on a search engine, use one of these SEO tools. You want to make a note of various metrics to evaluate and use as a baseline going forward:
• Current website traffic
• Number of organic keywords
• Keyword positions
• Average session duration
• Pages users exit most frequently
This is a good starting point, but depending on your goals and KPIs, you may have to delve into this a little more to select the metrics that best align with your goals.
You will also want to perform a site audit. This will consist of a variety of elements of your website:
• Indexing and Crawl Issues
• URL’s
• Page Titles
• Meta Tags
• Heading Tags
• Image Optimisation
• Internal and External Links
• Mobile Friendliness
• HTTPS Compliant
• Website Structure
• Domain Accessibility
• Website performance
• Schema Mark Ups
Once this is complete, you will have a good idea of how to structure the rest of the campaign. You can outline how much money you need to spend, as well as the time and effort required for the remainder of the campaign.
2. Website Performance & User Experience
Your website should be firing on all cylinders. Ensuring your website is performing at its peak must be at the forefront of the strategy. Search engines focus is on delivering the best experience for their users. A website that is slow and buggy will deliver a bad experience and will result in dropped rankings, so it is key to ensuring the performance of the website is at its highest.
You want to start by getting your website analysed by using tools like PageSpeed Insights or GTMetrix. Both tools will show you how your website is performing and if there are any areas of improvement. Use the findings from these tools to fix any issues.
The common areas that will help with performance are:
• Images – Compress or use other options such as Lazy Load.
• Caching – Server Caching or Content Delivery Network.
• Removing unused code.
• Redirects – Reducing the number of redirects on your website.
• Remove unused plugins.
The second element is user experience. Does your website appeal to the masses? Make sure your website is effective in the way that it provides users exactly with what they are looking for. Provide efficiency so that users don’t have to go through many pages to carry out an action and ensure an overall pleasant experience, leaving the users satisfied.
There are several ways to achieve this:
• Mobile-friendliness – over half of users visit websites using a mobile device. Use Google’s mobile-friendly tool to test.
• Website structure – All your webpages must be accessible within 3 clicks. Create a diagram of the structure of the website to identify issues.
• Fix indexing & crawl issues – Use Google Search Console to identify and remediate.
• URLs – Clear and concise URLs.
• Clear navigation.
• Use of breadcrumbs.
• Colour contrast and page layouts.
• Braking up long blocks of text.
3. Keywords
Keyword is like your compass; you will need keywords to measure how well your content is ranking. Using the right keywords to optimise your content is a sure-fire way of increasing your rankings.
Start by brainstorming some keywords around what you are selling/providing on your website. Then use tools like, Semrush, Ahrefs, Google and KWfinder to gather related keywords. Also, analyse which keywords your competitors are using that are performing well.
Then analyse all these keywords to get a better understanding of which ones can be used.
Keywords can be understood into the following segments:
Search Intent
Search Intent is about the purpose a user has when searching e.g. “Are home treadmills worth it”. This tells search engines that the user is aware of home treadmills but is unsure if they need one.
So, you can tailor the experience for this search intent. From this search intent, you can target the user to land on a piece of content explaining why home treadmills are worth it.
If a user searches “Buy home treadmills,” this is a good indication that the user is ready to buy, and you can target this keyword towards a product page.
Short-tail vs. long-tail keywords
Short-tail keywords are one or two words and long-tail keywords are longer.
A short-tail keyword does not describe the intent as well as a long-tail keyword. Long-tail keywords make it easier to guide users to the correct content, while short-tail keywords are slightly more difficult as they are broader.
As you begin your SEO campaign, you will want to target long-tail keywords first, as the search intent is easier to navigate. Also, long-tail keywords have less competition, making it easier to rank for them.
Once you have built up traffic to your website, you can then branch out to short-tail keywords.
Choosing your Keywords
You want to identify which keywords are relevant to you. Start with a handful of keywords, as selecting too many will make it difficult for search engines to understand what your content is about.
After using those keywords, go back and pick out another handful. Keep doing this, as you want to keep updating and optimising your content.
When creating content, do not follow the concept of creating content solely for search engines. With search engines focusing their efforts on providing the best results for users, they want content to be oriented towards the users. Therefore, create content for humans first. You want to generate content that is valuable to the end-user and is also naturally aligned with the human language.
Then, incorporate your keywords naturally. Utilising the keywords you have selected, choose one or two keywords to target and include them in the content. Add these to the page titles, heading tags, anchor text and anywhere else in the content where they fit naturally. Avoid forcing keywords anywhere, as search engines can detect this.
Maintaining a strategy of regularly updating your content is effective. Search engines aim to deliver the most recent and up-to-date content to their users. Consequently, updating your content regularly ensures your website remains at the top of the rankings.
5. Backlinks
Obtaining a backlink is a process of getting your content mentioned on a different website.
One of the main foundational principles of Google’s search engine is how they measure the importance of a website. They achieved this through a metric called PageRank. PageRank is a system for measuring importance based on the number of external websites linking to a particular website. This means that if another high-authority website links to your website, your website’s ranking will improve.
Since Google’s inception, PageRank has undergone significant changes and updates. Some argue that PageRank is no longer in use. However, the core principle remains to get your content mentioned on external websites.
To name a few ways to obtain backlinks:
• Identify and update broken\outdated links.
• Guest posting.
• Skyscraper technique.
• Forums.
• Publish comprehensive guides.
In simple terms, to gain domain authority, you will have to invest time in getting your content mentioned on third-party websites.
6. Measuring Progress
Measuring and tracking your progress is just as important as the other topics. Applying these techniques and then not checking whether any one of them has worked will not provide you insights into whether your hard work paid off. SEO takes time to fully manifest and show obvious signs. Therefore, you need to keep a constant eye on this.
Use the metrics and data that you noted down earlier to monitor and track these. If you feel like certain metrics have not improved, re-analyse, and adjust
Conclusion
SEO can be a long-term endeavour. Initially, you may not see significant improvements, but with patience and a solid strategy, you will undoubtedly reap the rewards.
This article aims to provide you with insight into key areas of an SEO strategy.
Based on your goals and niche, build a robust SEO plan that will work for you.
If you require any assistance, we are always ready to help. If you are a small business in the UK and looking for bespoke SEO services, Give us a call!